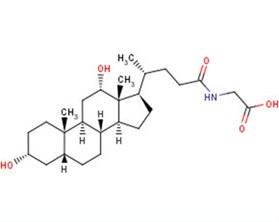
GLYCODEOXYCHOLIC ACID
CAS No. 360-65-6
GLYCODEOXYCHOLIC ACID( —— )
Catalog No. M20099 CAS No. 360-65-6
Glycodeoxycholic Acid is a bile acid that induces severe pancreatitis in rats. It can induce the apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameGLYCODEOXYCHOLIC ACID
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionGlycodeoxycholic Acid is a bile acid that induces severe pancreatitis in rats. It can induce the apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells.
-
DescriptionGlycodeoxycholic Acid is a bile acid that induces severe pancreatitis in rats. It can induce the apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number360-65-6
-
Formula Weight449.63
-
Molecular FormulaC26H43NO5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESC[C@H](CCC(=O)NCC(O)=O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@]12C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.CHEN Jiang et al. The effect of glycodeoxycholic acid on P53 expression in the apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells. Chinese Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science 2009 27(3):167-169.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Delta 5-avenasterol
Delta 5-avenasterol has antioxidant activity.
-
Diethyl phosphate
Diethyl phosphate a Non-Specific Metabolite of Organophosphorus Pesticides.
-
Poricoic acid G
Poricoic acid G shows inhibition of tumor-promoting effects and cytotoxic activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


